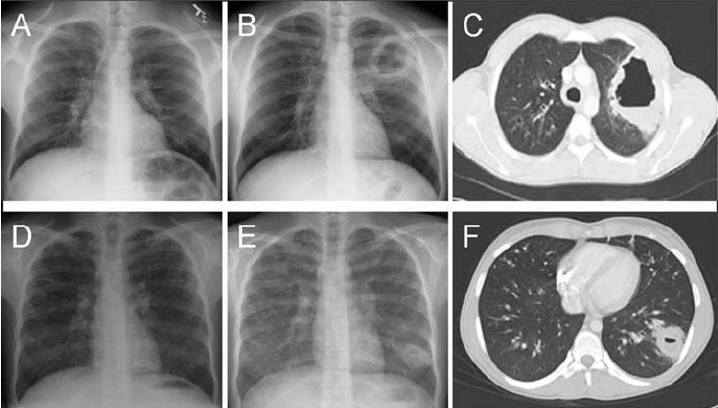
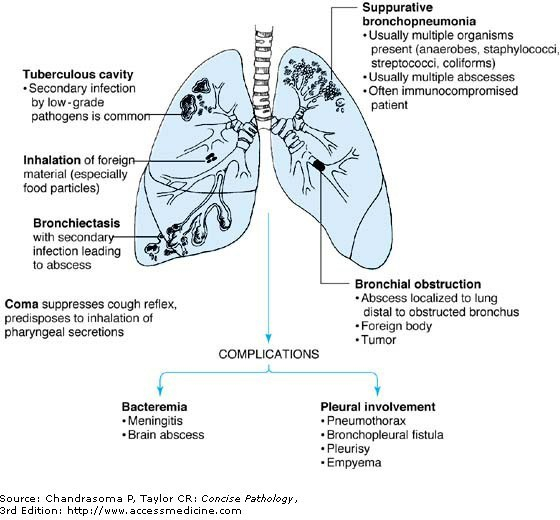
Causes
- aspiration of oropharyngeal contents
- in patients predisposed to lose consciousness
- alcoholics, epileptics, comatosed
- cavitations may occur ; air-fluid levels on CXR
- due to anaerobes (eg, Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, Peptostreptococcus) or S aureus
- in patients predisposed to lose consciousness
- bronchial obstruction (eg, cancer)
- complication of bacterial pneumonia (necrotizing)
- nosocomial ; caused by S.aureus, E. coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- secondary to TB / bronchiectasis
- hematogenous spread of infection
- in patients with septicemia or infectious endocarditis (septic emboli)
- often multiple and monomicrobial
- most common causative agents being Staph and Strep
Mechanism
- Lysosomal enzymes serve to digest the offending pathogens and tissue debris, as well as to chemotactically summon additional neutrophils or macrophages to the area
- Occasionally, however, the enzymes will also damage the surrounding parenchyma, setting the stage for abscess formation
- Suppurative destruction : necrosis secondary to the release of lysosomal enzymes by neutrophils and macrophages
Location
Lung abscess 2° to aspiration is most often found in right lung. Location depends on patient’s position during aspiration:
- Upright = basal segments of right lower lobe
- Supine = posterior segments of right upper lobe or superior segment of right lower lobe